Title: Understanding Stock Market Basics: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction to Stock Market
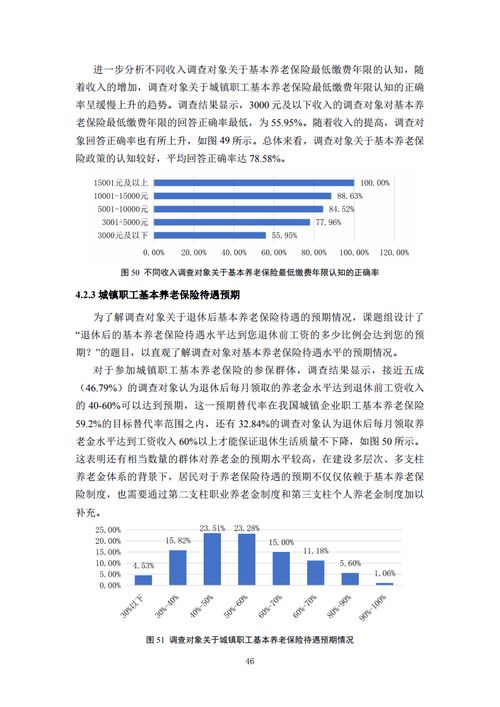
The stock market, often referred to as equity market, is a platform where investors buy and sell shares of publicly traded companies. It serves as a crucial component of the economy, facilitating capital formation and enabling companies to raise funds for growth and expansion. Understanding the basics of the stock market is essential for both seasoned investors and beginners alike.
Key Concepts in Stock Market
1.
Stocks and Shares
: Stocks represent ownership in a company, and each unit of ownership is called a share. When you buy shares of a company, you become a shareholder, entitling you to a portion of the company's assets and profits.
2.
Stock Exchanges
: Stock exchanges are centralized platforms where buyers and sellers come together to trade stocks. Examples include the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), Nasdaq, London Stock Exchange (LSE), and Tokyo Stock Exchange (TSE).
3.
Stock Indices
: Stock indices are statistical measures used to track the performance of a specific group of stocks. Examples include the S&P 500, Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA), and FTSE 100. These indices provide insights into the overall market trends.
4.
Bull vs. Bear Market
: A bull market refers to a period of rising stock prices and investor optimism, while a bear market indicates a period of falling prices and pessimism. Understanding market cycles is crucial for making informed investment decisions.
5.
Market Order vs. Limit Order
: A market order instructs the broker to buy or sell a stock at the current market price, while a limit order sets a specific price at which the trade should be executed. Each order type has its advantages and risks.
Factors Influencing Stock Prices
1.
Company Performance
: The financial performance of a company, including its earnings, revenue growth, and profitability, directly impacts its stock price. Investors closely monitor quarterly earnings reports and other financial metrics to assess the company's health.
2.
Market Sentiment
: Investor sentiment, influenced by factors such as economic indicators, geopolitical events, and news headlines, can drive stock prices in the short term. Market sentiment can be irrational at times, leading to price fluctuations.
3.
Industry Trends
: Industryspecific factors, such as technological advancements, regulatory changes, and consumer preferences, affect stock prices within a particular sector. Understanding industry dynamics is essential for sectorspecific investments.
4.
Macroeconomic Factors
: Economic indicators like GDP growth, inflation rate, interest rates, and unemployment levels have a significant impact on overall market sentiment and stock prices. Investors analyze macroeconomic data to gauge the direction of the market.
Investment Strategies
1.
LongTerm Investing
: Longterm investors aim to build wealth gradually over time by buying and holding quality stocks for years or even decades. This strategy requires patience, discipline, and a focus on fundamental analysis.
2.
Value Investing
: Value investors look for undervalued stocks trading below their intrinsic value. They believe that the market sometimes misprices stocks, providing opportunities to buy quality companies at a discount.
3.
Growth Investing
: Growth investors focus on companies with strong growth potential in terms of earnings, revenue, and market share. They are willing to pay a premium for highgrowth stocks with promising future prospects.
4.
Dividend Investing
: Dividend investors seek stocks that pay regular dividends, providing a steady stream of income. They prioritize companies with a history of consistent dividend payments and sustainable payout ratios.
Risk Management
1.
Diversification
: Diversifying your investment portfolio across different asset classes, sectors, and geographical regions can help reduce risk. By spreading your investments, you minimize the impact of poor performance in any single investment.
2.
Risk Assessment
: Assessing your risk tolerance and investment goals is crucial for determining the appropriate asset allocation and investment strategy. Consider factors such as age, financial situation, and investment timeline when evaluating risk.
3.
StopLoss Orders
: Implementing stoploss orders can help mitigate losses by automatically selling a stock if it falls below a predetermined price level. This risk management tool protects investors from significant downside risk.
4.
Research and Due Diligence
: Conduct thorough research and due diligence before making investment decisions. Evaluate company fundamentals, industry trends, and market conditions to make informed choices and avoid unnecessary risks.
Conclusion
The stock market offers investors opportunities for wealth creation and capital appreciation, but it also involves inherent risks. By understanding the fundamentals of the stock market, including key concepts, factors influencing stock prices, investment strategies, and risk management techniques, investors can make informed decisions and navigate the market with confidence.
Investing in stocks requires patience, discipline, and a longterm perspective. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced investor, continuous learning and staying informed about market developments are essential for achieving financial success in the stock market.
Remember, investing involves uncertainty, and past performance is not indicative of future results. By following sound investment principles and staying true to your investment objectives, you can build a resilient and diversified portfolio that stands the test of time.
References
Investopedia. (n.d.). Stock Market Basics: A Beginner's Guide to Trading Stocks. Retrieved from [https://www.investopedia.com/investing4689728](https://www.investopedia.com/investing4689728)
The Balance. (n.d.). How to Invest in Stocks: A StepbyStep for Beginners. Retrieved from [https://www.thebalance.com/howtoinvestinstocks2466642](https://www.thebalance.com/howtoinvestinstocks2466642)
CNBC. (n.d.). Understanding Stock Market Basics. Retrieved from [https://www.cnbc.com/stockmarketbasics/](https://www.cnbc.com/stockmarketbasics/)
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. (n.d.). Beginners' Guide to Investing. Retrieved from [https://www.investor.gov/introductioninvesting/investingbasics/beginnersguidetoinvesting](https://www.investor.gov/introductioninvesting/investingbasics/beginnersguidetoinvesting)
